NanoEngineers Aim to Grow Tissues with Functional Blood Vessels
San Diego, Nov. 15, 2010 -- University of California, San Diego NanoEngineers won a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to develop the tools to manufacture biodegradable frames around which heart tissues – functional blood vessels included – will grow. Developing methods for growing tissues that mimic nature’s fine-grained details, including vasculature, could lead to breakthroughs in efforts to grow replacement cardiac tissues for people who have suffered a heart attack. The work could also lead to better systems for growing and studying cells, including stem cells, in the laboratory.
|
“We are creating biomaterials with nanostructures on the inside,” said Chen. “Scientifically there are so many opportunities at the molecular level, and nanoengineering is a perfect fit for that. We expect our new biofabrication platform will yield tissues that mimic natural tissues much more closely.”
One such opportunity is to add new levels of precision and functionality to the scaffolds produced by the “biofabrication platform” that Chen and his collaborators invented and have been improving over the last five years.
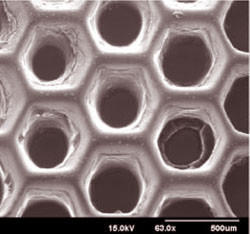
With the improved biofabrication platform, engineers in the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering's Department of NanoEngineering -- based on the second floor of Calit2's Atkinson Hall -- will be able to produce scaffolds with precisely designed systems of nanoscale pores and other microarchitectural details that control how cells interact with each other and with the environment.
“You need to design the pores so the cell can get nutrition and dump waste…pathways for the cell to survive in the system,” explained Chen.
|
In addition, the chemical properties of the new scaffolds will change from top to bottom, which will create chemical gradients that drive cell growth.
As in previous versions of Chen’s scaffold-building system, cells will be encapsulated within scaffold walls.
“Usually, when researchers grow tissue, they make a scaffold, put the cells in the scaffold and let the cells grow,” explained Chen. “When we fabricate our scaffolds, the cells are already inside the scaffold walls.” Encapsulating cells within the walls encourages uniform seeding of cells.
The scaffolds will be based on natural materials such as hyaluronic acid, a key component of the “extracellular matrix” that provides structural support, wound healing, and a range of other functions to human and other animal tissues.
“The hydrogels for our scaffolds can’t be too soft, too sticky or too rigid. They need to fit the needs of the biological tissue,” said Chen.
Collaborators at Harvard Medical School will grow and characterize the tissues started on the scaffolds.
Projection Bioprinting
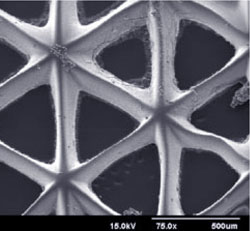
To manufacture tissue scaffolds, Chen and colleagues have developed and continue to refine a manufacturing process that uses light, precisely controlled mirrors, and a computer projection system. First, the engineers design a three dimensional model of the structure to be printed. Next, the engineers prepare a solution containing both the cells that will eventually grow into the tissue and the polymers that will solidify into the scaffold. When light shines into the solution using the series of mirrors, the scaffold solidifies according to the exact specifications of the projected image.
Following these steps, scaffolds are manufactured and cells are encapsulated in scaffold walls as light solidifies the polymers one layer at a time.
“With our biofabrication platform, we can build arbitrary, three-dimensional shapes, like branches of blood vessels, and tubes – large and small,” said Chen. My focus is on the materials fabrication and devices level. This work is applicable to many different types of cells and tissues.”
Media Contacts
Daniel Kane, (858)534-3262 or dbkane@ucsd.edu
Related Links